m (Corrected numbering.) |
(Finished comments on boot.php, and added isolinux.cfg for esxi) |
||
| Line 411: | Line 411: | ||
} | } | ||
?> | ?> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
-- | |||
* This tries to load a esxi51.ipxe file first, which is basically the rest of whats here, but just another place I was playing around with. | |||
* The above way to load ESXi, tries to use iPXE's native multiboot, however this currently fails. [http://lists.ipxe.org/pipermail/ipxe-devel/2012-September/001846.html See this iPXE mailing list thread] for more information. | |||
-- | |||
=== isolinux.cfg (esxi) === | |||
* I made a quick and simple file that loads the installer immediately, instead of hitting the default boot menu | |||
* In addition to the above, [http://www.vcritical.com/2011/07/vmware-esxi-5-interactive-pxe-installation-improvements/ you also need to make some other modifications] (that link also contains the other part of the instructions to get it all setup -- basic instructions to get the installer to PXE boot) | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash" line="GESHI_NORMAL_LINE_NUMBERS"> | |||
DEFAULT install | |||
LABEL install | |||
KERNEL mboot.c32 | |||
APPEND -c boot.cfg | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 18:15, 13 October 2012
Intro
PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) Booting, or just Network booting in general is very interesting, at least to me, and a few others. As I believe it was Marty Connor in this awesome video "gPXE: Modern FOSS Network Booting" said that some people get really excited over booting machines over networks (including the Internet!) while others... not so much.
Well, I'm one of those people who gets really excited over the idea of booting machines over a network, and I can't really put my finger on why, it's just awesome to me.
So, I wanted to document the netboot setups that I use at my home, and my work. This entry consists of my home network. My work one, I'll put in another entry (as it's significantly different in it's programming, but does the same functions), and link here.
Now, network booting isn't for everyone, and it doesn't fit every situation, so your mileage will vary greatly.
My home network consists of iPXE, PHP scripting, and separate utilities. All of this is detailed below... so lets begin!
What does this page assume?
- You have a working network
- You control your DHCP Server
- You have control of your DNS server
- You have a working webserver
- Basic understanding of PHP
- Have a basic understand of whats involved with PXE Booting, even if it's skimming over the Wikipedia page
- Have a machine that is capable of picking the network card to boot from, via PXE (On most Dell systems, you need to go into the BIOS, Integrated Peripherals, and mark the NIC as "On W/ PXE", not just "On", or "On W/ ImageServer"
My Environment
- Linux, Distro: Gentoo (~AMD64 "Unstable")
- Apache 2.4.3
- PHP 5.4.7
- tftp-hpa 5.2
- iPXE (current GIT master)
- Misc Utilities like Drive Fitness Test, SeaTools, Memtest, etc.
The Basic Process
-- My Setup
- Computer powers on, and selects the NIC to boot from, either via interaction, or it being the first device
- The native PXE Stack (iPXE (flashed onto the ROM/BIOS), Intel, Broadom, Realtek, etc) brings up the network card, does a DHCP Request, while also requesting, at least, options 66 and 67
- DHCP Server responds with an IP, and the two options
- The PXE Stack then tried to contact the server provided in option 66, to retrieve the file specified in option 67, which in this case is iPXE (for non-iPXE clients), over TFTP
- iPXE then unloads the native PXE stack (to a degree), and takes over, issuing it's own DHCP Request, again requesting, among other options, 66 and 67
- The DHCP Server responds with (typically) the same IP address, but now detects that the client is iPXE, and passes a different option 67.
- iPXE then boots to the URL passed in option 67 this time (via HTTP), and that script then directs it what to do.
Files
dhcpd.conf
- This information can be placed globally, specific subnets, or individual filename/next-server can be placed on host definitions
- Relevant sections of my ISC DHCP config:
if exists user-class {
if option user-class = "iPXE" {
filename "http://boot.example.com/preboot.php";
}
} else {
filename "ipxe.kkpxe";
}
next-server 10.0.3.2;- This if statement breaks the "infinite loop"
- The filename listed on line 3 is for when iPXE does the DHCP request
- The filename listed on line 6 is for when a non-iPXE client does a DHCP request, to get it to use iPXE
- The next-server on line 8 is the TFTP server that the non-iPXE clients will grab the above file from
ipxe.kkpxe
- This file is built from the iPXE source, running "make bin/ipxe.kkpxe", then copying the bin/ipxe.kkpxe file to your TFTP server's root directory
01_boot_vhost.conf
- This is placed in /etc/apache2/vhosts.d, to configure the boot.example.com vhost
- This configures your virtual host (boot.example.com from above), to point to where you want to store your files. I choose to keep mine in the TFTP root, under the "netboot" folder, so everything related to the netboot is contained in that folder.
<VirtualHost boot.example.com:80>
ServerName boot.example.com
DocumentRoot "/tftp/netboot/"
<Directory "/tftp/netboot">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>preboot.php
- This is the file that the iPXE client first grabs to see what it needs to do
<?php
echo "#!ipxe\n";
echo "chain http://".$_SERVER['SERVER_NAME']."/boot.php?MAC=\${netX/mac}";
?>- So this is an extremely simple file, as you can tell. It's purpose is to pass the MAC address of the booting network card off to the boot.php script. So this references the same server name (pulls it in from the PHP variables), and then uses the ${netX/mac} iPXE variable to pull the MAC of the active network card, via GET (Variables in the URL).
boot.php
- This is the big guy, so I'm going to do some inline comments to explain it
<?php
$mac = "";
$servername = $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];
if (isset($_GET['MAC'])) {
$mac = $_GET['MAC'];
}
header ( "Content-type: text/plain" );--
- The above sets some variables, and grabs them from the URL, if they are set, and sets the content-type.
--
if ( $mac != "" ) {
switch ($mac) {
case "00:0c:29:xx:xx:xx":
case "00:e0:b8:xx:xx:xx":
// Testing VM
ipxemenu();
break;
case "bc:ae:c5:xx:xx:xx":
echo "#!ipxe\n";
// Atom - Living Room Frontend
echo "kernel http://boot.example.com/bzImage-Atom ip=dhcp root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=10.0.3.2:/nfsroot/hdfe,nfsvers=3,tcp,hard,intr,nolock vga=0x317 quiet\n";
// splash=silent,theme:MythTV quiet console=tty1\n";
// echo "initrd http://boot.example.com/fe1-initrd.img\n";
break;
case "00:10:18:xx:xx:xx":
echo "#!ipxe\n";
// Athlon 64 HDFE - Bedroom Frontend
echo "kernel http://boot.example.com/bzImage-A64 ip=dhcp root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=10.0.3.2:/nfsroot/hdfe1,nfsvers=3,tcp,hard,intr,nolock vga=0x317\n";
//splash=silent,theme:MythTV quiet console=tty1\n";
//echo "initrd http://boot.example.com/fe1-initrd.img\n";
break;
default:
ipxemenu();
break;
}
echo "boot";
} else {
exit();
}--
- This is where the fun begins!
- First, it makes sure a MAC address is set, otherwise it just exits to an empty file
- Then it searches to see if there are special per-MAC instructions to do. In the above example, the first two MACs run the ipxemenu() function, that I was using for testing
- The next two are two different MythTV Frontends I have in our apartment. These netboot to a NFSRoot, so you can see how to have iPXE directly load Linux over HTTP
- Then if all else fails (usual), run the ipxemenu() function to present the iPXE menu. (Here I use to have stuff to chain to pxelinux.0, and load a vesamenu up, but I recently switched to iPXE's menu. For pxelinux integration, see my work menu)
--
function ipxemenu() {
echo "#!ipxe\n";
echo ":menustart\n";
echo "menu iPXE Boot Menu\n";
echo "item --gap -- Diagnostics\n";
echo "item memtest Memtest86+\n";
echo "item dft Drive Fitness Test\n";
echo "item spinrite Spinrite\n";
echo "item hdt Hardware Detection Tool\n";
echo "item b57 b57 Diags\n";
echo "item qwipe Quick Wipe\n";
echo "item --gap -- Internet Boots\n";
echo "item ipxedemo iPXE Demo Boot\n";
echo "item ritboot rit.edu clone of boot.kernel.org\n";
echo "item --gap -- Live Systems\n";
echo "item gparted GParted\n";
echo "item smartos SmartOS\n";
echo "item --gap -- WinPE\n";
echo "item peboot Windows PEBoot via SANBoot\n";
echo "item wimboot Windows PEBoot via WIMBoot\n";
echo "item --gap -- Installers\n";
echo "item esxi5 ESXi 5.1 Installer\n";
echo "item esxi5sl ESXi 5.0 Installer via PXELinux\n";
echo "item freedos FreeDOS 1.1\n";
echo "item vesamenu Vesamenu\n";
echo "item --gap -- Other PXE Systems\n";
echo "item wds Windows Deployment Services\n";
echo "item shell iPXE Shell\n";
echo "item sanhook Sanhook test on FreeNAS\n";
echo "choose os && goto \${os}\n";
echo ":shell\n";
echo "shell\n";
esxi5sl();
sanhook();
qwipe();
b57();
freedos();
smartos();
gparted();
wds();
hdt();
memtest();
ipxedemo();
ritboot();
dft();
spinrite();
sanbootpe();
wimbootpe();
vesamenu();
esxi5();
echo ":end\n";
}--
- This is the function that creates the main iPXE menu
- You can check the full syntax from the link above, but it's fairly simple
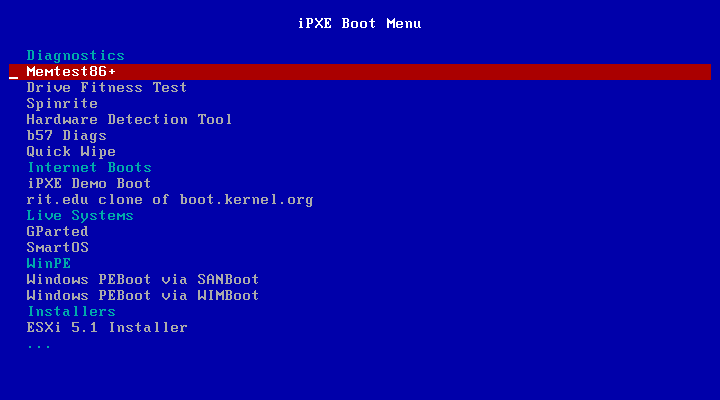
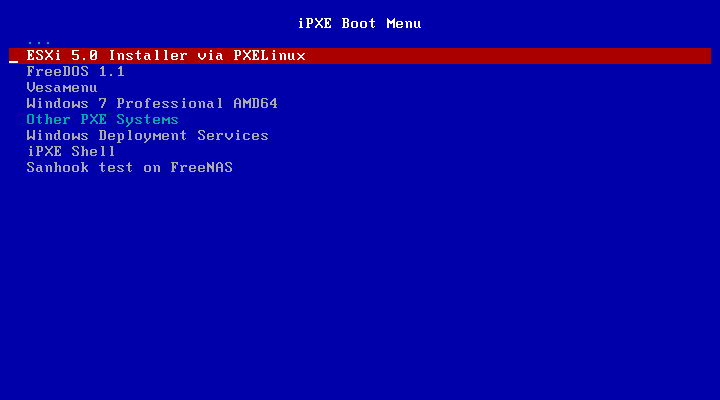
- This creates the menu that is seen when the client is booted. It looks something like this:
- Once the menu is created, it calls the different functions to include the goto markers, otherwise the menu will fail is that option is selected. I choose to do it this way, with the intention of eventually adding options where the menu can be dynamic depending on the machine
- I also added a :end goto marker, at the end, as I found pxelinux needed this to boot, otherwise it continued on through this menu (i.e. booting the option that was placed after it)
- Most of the below, you can find really good documentation on the iPXE website. However, I will note anything special as needed
--
function sanhook() {
echo ":sanhook\n";
echo "sanhook iscsi:10.0.3.107::::iqn.2011-03.example.org.istgt:test\n";
echo "sleep 5\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function esxi5sl() {
echo ":esxi5sl\n";
echo "set 210:string http://boot.example.com/esxi5/\n";
echo "set 209:string isolinux.cfg\n";
echo "chain http://boot.example.com/pxelinux.0\n";
echo "goto end\n";
}--
- This boots the ESXi installer via Syslinux (pxelinux/mboot). I found this way currently works.
- This will be documented as other files, below.
--
function qwipe() {
echo ":qwipe\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0x00 --no-describe http://boot.example.com/wipe2.img\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function b57() {
echo ":b57\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0xa0 --no-describe http://boot.example.com/B57udiag-15.23.iso\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function freedos() {
echo ":freedos\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0xa0 --no-describe http://boot.example.com/fd11src.iso\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function smartos() {
echo ":smartos\n";
echo "kernel smartos/platform/i86pc/kernel/amd64/unix -B console=text,standalone=true,noimport=true,root_shadow='\$5\$2HOHRnK3\$NvLlm.1KQBbB0WjoP7xcIwGnllhzp2HnT.mDO7DpxYA'\n";
echo "module smartos/platform/i86pc/amd64/boot_archive\n";
echo "boot\n";
echo "sleep 10\n";
}
function wds() {
echo ":wds\n";
echo "set net0/next-server 10.0.3.99\n";
echo "chain tftp://10.0.3.99/boot%5Cx86%5cwdsnbp.com\n";
echo "sleep 10\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}--
- This one a lot of people may be interested in. This will chain to a Windows Deployment Services.
- Things to note here, the wdsnbp.com looks at the next-server in the dhcp packets for where to talk to, well, this may not actually be your windows server, it is not in my case. This sets the next-server to the WDS Server, then chains to it, so that it boots properly.
- Also note the hex in the tftp URL. This is needed, as it's a Windows TFTP Server, so it's actually in the path of boot\x86\wdsnbp.com
- TODO? Use iPXE arch detection to boot 64bit?
--
function gparted() {
echo ":gparted\n";
echo "kernel http://boot.example.com/gparted/live/vmlinuz boot=live config union=aufs noswap noprompt fetch=http://boot.example.com/gparted/live/filesystem.squashfs\n";
echo "initrd http://boot.example.com/gparted/live/initrd.img\n";
echo "boot\n";
echo "sleep 10\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function hdt() {
echo ":hdt\n";
echo "sanboot --no-describe --drive 0x00 http://boot.example.com/hdt-0.5.0.img\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function spinrite() {
echo ":spinrite\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0xa1 --no-describe http://boot.example.com/spinrite.iso\n";
echo "goto menustart\n";
}
function ipxedemo() {
echo ":ipxedemo\n";
echo "chain http://boot.ipxe.org/demo/boot.php\n";
}
function ritboot() {
echo ":ritboot\n";
echo "set 209:string pxelinux.cfg/default\n";
echo "set 210:string http://boot.rit.edu/bko/\n";
echo "chain http://boot.rit.edu/bko/pxelinux.0\n";
echo "goto :menustart\n";
}
function dft() {
echo ":dft\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0x00 http://boot.example.com/dft32_v416_b00_install.IMG\n";
}
function memtest() {
echo ":memtest\n";
echo "chain http://boot.example.com/memtest.0\n";
}--
- This is the memtest.0 NBP from iPXE (patches were submitted to memtest, but I don't think they included them yet).
--
function sanbootpe() {
echo ":peboot\n";
echo "set keep-san 1\n";
echo "sanboot --drive 0x81 http://boot.example.com/PEBoot-07_08_11.iso\n";
}
function wimbootpe() {
echo ":wimboot\n";
echo "kernel wimboot\n";
echo "initrd winpe/Boot/bootmgr.exe bootmgr.exe\n";
echo "initrd winpe/Boot/BCD BCD\n";
echo "initrd winpe/Boot/boot.sdi boot.sdi\n";
echo "initrd winpe/Boot/boot.wim boot.wim\n";
echo "imgstat\n";
echo "boot\n";
}--
- wimboot is a much better way of booting WinPE via iPXE. It's extremely quick, and saves memory!
--
function vesamenu() {
echo ":vesamenu\n";
echo "set 210:string http://boot.example.com/\n";
echo "set 209:string mainmenu.gpxe\n";
echo "chain \${210:string}pxelinux.0\n";
}
function esxi5() {
echo ":esxi5\n";
echo "chain http://boot.example.com/esxi51/esxi51.ipxe\n";
echo "echo failing back\n";
echo "goto end\n";
echo "set base-url http://boot.example.com/esxi5/\n";
echo "kernel \${base-url}tboot runweasel\n";
echo "module \${base-url}b.b00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}useropts.gz\n";
echo "module \${base-url}k.b00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}a.b00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v02\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v03\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v04\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v05\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v06\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ata-pata.v07\n";
echo "module \${base-url}block-cc.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ehci-ehc.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}s.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}weaselin.i00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ima-qla4.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ipmi-ipm.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ipmi-ipm.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ipmi-ipm.v02\n";
echo "module \${base-url}misc-cni.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}misc-dri.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-be2n.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-bnx2.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-bnx2.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-cnic.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-e100.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-e100.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-enic.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-forc.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-igb.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-ixgb.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-nx-n.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-r816.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-r816.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-s2io.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-sky2.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}net-tg3.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}ohci-usb.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-ahc.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-ata.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-sat.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-sat.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-sat.v02\n";
echo "module \${base-url}sata-sat.v03\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-aac.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-adp.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-aic.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-bnx.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-fni.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-hps.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-ips.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-lpf.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-meg.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-meg.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-meg.v02\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-mpt.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-mpt.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-mpt.v02\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-qla.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-qla.v01\n";
echo "module \${base-url}scsi-rst.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}uhci-usb.v00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}tools.t00\n";
echo "module \${base-url}imgdb.tgz\n";
echo "module \${base-url}imgpayld.tgz\n";
echo "imgstat\n";
echo "boot\n";
}
?>--
- This tries to load a esxi51.ipxe file first, which is basically the rest of whats here, but just another place I was playing around with.
- The above way to load ESXi, tries to use iPXE's native multiboot, however this currently fails. See this iPXE mailing list thread for more information.
--
isolinux.cfg (esxi)
- I made a quick and simple file that loads the installer immediately, instead of hitting the default boot menu
- In addition to the above, you also need to make some other modifications (that link also contains the other part of the instructions to get it all setup -- basic instructions to get the installer to PXE boot)
DEFAULT install
LABEL install
KERNEL mboot.c32
APPEND -c boot.cfg